
Now we need to head to the switch to set up things. Settings: Leave blank to have the client use the default data VLAN defined on the switchport, or use the attributes mentioned above (Standard RADIUS attributes) to send a specific VLAN to the device.
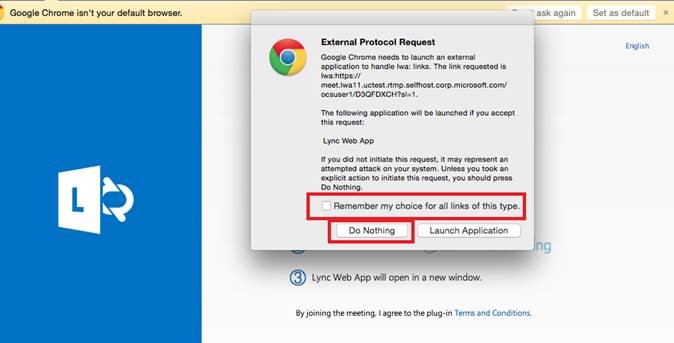
If you like you can override and rather send the VLAN assignment (instead of relying on the switch interface setting) using “Standard RADIUS” attributes, like this:Ĭonditions: This will apply to all clients that belong to AD user group Domain Users and that are authenticating from a switch in my network (based on regex for the IP address).Ĭonstraints: Choose PEAP for authentication method. This makes the device use the voice VLAN specified for the switchport. Choose “Vendor Specific” attributes, “Cisco” as the vendor and enter the value “device-traffic-class=voice”. Settings: What is sent back to the device. Under overview: Enter a policy name and leave default.Ĭonditions: This policy will apply to all clients being authenticated from a LAN switch (regex IP syntax) and only users/devices that belong to the AD group for dot1x Mac Auth BypassĬonstraints: Only PAP unencrypted authentication will work with MAB. Under Network Policies, make sure we define two policies – one for MAB and one for dot1x – and place them above any “Deny Access” policies in the policy order.įirst off, the MAB policy. Settings: Make sure that we leave the authentication specifics to the Network Policy, so do not override. Regex pattern is ^10\.0\.107\.+$ which will basically cover all IP addresses in the 10.0.107.0 subnet – which all of my switches belong to. Overview: Enter a policy name and leave the rest to default.Ĭonditions: Here I have used a regex pattern that will match any switch management IP. The Network Policy defined afterwards will be more fine grained as to what conditions are required FROM the clients and any settings to send back TO the clients. Shared secret must match the key entered in the RADIUS server definition on the switch. Under RADIUS clients, enter the IP address of the authenticator switch. Under Server Manager and NPS management, do the following: Next we need to set up the RADIUS server, where the devices ultimately will be accepted or rejected for network access. As an extra security concern, remove any other security group membership, like the default Domain Users: Password: MAC address, all lower case letters.Ĭreate a Security Group and add the devices to this. User name: MAC address, all lower case letters. To have devices authenticate we need to define AD users for them by their MAC addresses:
#LYNC FOR MAC REQUEST CONTROL INSTALL#
I will be using a Windows Server with Network Access and Policy Server (NPS) service, as it requires no extra license and is included with the Windows server – you only need to install the role on the server (not covered here). This is simply explained a method where the phone can authenticate by it’s MAC address. In order to setup authentication for Lync phones we will have to use another authentication method called MAC Authentication Bypass, or MAB.
#LYNC FOR MAC REQUEST CONTROL HOW TO#
This is of course no good to us now that we have learned how to separate the phone and PC in different VLAN’s.

This way both phone and PC are put in the same VLAN when authenticated (also known as multi-host mode). One workaround is to have the PC authenticate both devices, but then you cannot use the phone without the PC. They will relay dot1x requests to connected PC’s but cannot authenticate themselves. The first issue we face is that Lync Phones do not support dot1x.
Let’s move on to dot1x authentication, which is slightly more complex to implement. This is useful both for address management (separate subnets) as well as security – where you isolate the devices to avoid packet sniffing, eavesdropping etc. Any PC attached to the phone will be put in the data VLAN we defined. Make sure you have a DHCP server offering address and options in that VLAN. Now you just need to reset the interface (shutdown / no shutdown) and the phone will pick up the new assigned VLAN. The interface then needs to be told what VLAN to assign voice and data devices that connects: # This makes LLDP run on the switch, so that phones can learn the voice VLAN info from the switch Luckily, Cisco also has support for LLDP and only needs to be enabled on the switch: Lync Phone manufacturers rather use the industry standard Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) for this. CDP is also used to discover that the device is PoE enabled and offer Power over Ethernet to it if the switch supports it. Cisco primarily offers their own Discovery Protocol (CDP) to teach IP phones about specific voice VLAN assignments on the connected switch port. There was little to nothing on the subject to be found online, so I thought I would share my experiences. In a recent project I have been working on voice VLAN implementation and 802.1x (or dot1x) authentication in our Cisco switching infrastructure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
